Healthcare data warehouse benefits, features, and use cases
The healthcare industry generates an unprecedented amount of data each year — approximately one-third of the world’s total data volume. This data holds the power to drive informed decision-making, yet a staggering 97% of it goes unused.
As technology increasingly addresses the challenges of harnessing this data, the healthcare data warehouse emerges as a popular tool for aggregating and analyzing data. This article provides a detailed overview of this software, including:
What is a healthcare data warehouse?
In simple terms, a healthcare data warehouse (HDW) is an organized central repository for all aggregated, usable healthcare information retrieved from multiple sources like:
- Electronic health records (EHRs)
- Electronic medical records (EMRs)
- Enterprise resource planning systems (ERPs)
- Radiology
- Lab databases
- Wearables
- Population-wide data
It's important to keep in mind that an HDW is only one key component of an integrated healthcare data platform, which includes a connectivity layer, data lake, analytics and enrichment layer, data warehouse, and integrations and reporting features. These platform processes compose a data platform pipeline that collects and transforms raw data into usable analytics for your organization’s decision-making.
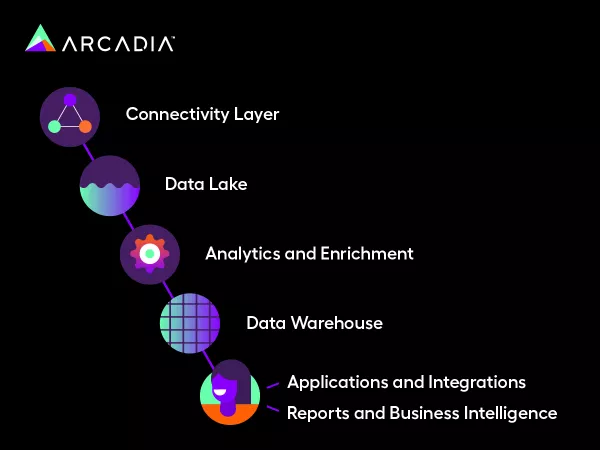
Here’s how an HDW fits into the data platform pipeline:
- Data is collected in a connectivity layer, which is built from various use cases, types, and fields. This layer determines exactly how much data you need, and your platform could take days to collect your data volume.
- All collected data is stored in a data lake in its raw condition and is currently not primed for meaningful analytics.
- The data lake undergoes analytics and enrichment for conversion into usable metrics. This is usually done by a software provider and includes the active management of thousands of quality measures such as risk adjustment, risk suspecting, and cost utilization.
- Usable data is stored in an HDW as a central location for consistent, organized, and accurate data recovery.
- Usable data is pulled from the HDW for business intelligence dashboard reporting through a collaboration between analysts and providers.
- Specified applications and integrations are leveraged to build views that align with your organization’s needs.
HDWs are the fourth component of a healthcare data platform, and the prior components directly influence it. In other words, the connectivity layer, data lake, and analytics enrichment processes determine the volume and type of data stored in an HDW.
It’s worth distinguishing between a data lake and an HDW, as you want these two components to remain separate. A data lake represents raw data in its unusable form, while an HDW is an organized storage location of usable data.
Building an efficient HDW takes precision, but the benefits can revolutionize your current care workflows, as you’ll see in the next section.
What are the benefits of healthcare data warehousing?
Now that you know how an HDW functions within the data platform pipeline, you might wonder about its practical benefits.
When you leverage an HDW correctly, you’ll experience benefits like:
- Efficient reporting: HDWs can help your team create precise analytics reports quickly to get a bird’s eye view of your performance. For example, your team can use dashboard reporting to efficiently compare your high-cost members based on cohort (admission, drug, condition, etc.), total members, and total cost.
- Improved clinical decision-making: Discover the right insights at the right time by accessing a unified HDW. Rather than siloed databases, an HDW can connect all of your information in a supportive, evidence-based clinical decision framework.
- Optimized insurance claims and payments: Your healthcare organization can review and efficiently process large sums of claims data, access its compensation services, prevent fraud, and ameliorate underlying roadblocks.
- Elevated strategic planning: Take a comprehensive approach to resource planning with accessible data tools. Use data gathered from disparate sources to prevent future issues.
- Enhanced patient satisfaction and outcomes: In your patients’ eyes, an accessible HDW means that they can receive timely and accurate treatment derived from advanced analytical models and experience measurable progress.
- Personalized value-based care: Collaborate with other clinicians using a uniform HDW to generate deeper insights and enhance current treatment plans for patients while avoiding unnecessary costs.
HDWs can help you identify and achieve your organization’s goals. Additionally, they can improve your day-to-day workflows so you can focus on delivering the highest quality care at the most opportune time.
What are the key features to look for in a healthcare data warehouse?
HDWs are inherently sensitive and require proper handling to meet security measures while integrating successfully with various data sources. Additionally, each HDW is tailored to a specific organization’s needs, so the key features will differ depending on the HDW’s proposed end-use.
However, there are common aspects worth paying attention to, regardless of your team’s custom HDW model. A fully functioning HDW will include:
- Data integration: HDWs field data from EHRs, ERP software, HR management systems, claims management systems, and large public health databases. This data integration includes big data and streaming data in addition to advanced medical data loading and querying. Make sure your HDW is equipped to standardize data from both internal and external sources.
- Data quality: Successful HDWs include quality controls for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Built-in processes like data cleaning and validation help to promote standardization across data points.
- Scalability: Your organization could start with a relatively simple HDW configuration, but with increased use, you will likely need to rely on a scalable solution. A robust HDW built with future data volume in mind will help you make sense of larger data loads.
- Security and privacy: Correctly built HDWs have encryption and access controls to protect patient data. Raw-level permissions by account or patient ownership keep HDWs aligned with US Federation laws, such as HIPAA.
- Interoperability: Efficient HDWs make fragmented workflows a thing of the past by bringing operational care teams together to collaborate for whole-person care. Your HDW should be set up with care coordination ease in mind.
If you decide to go with a single or multi-data platform provider, verify that they offer the above features. Or, if you decide to advise an in-house team, build your data platform with these outlined aspects. That way, you can maximize your analytical horsepower and generate the highest ROI for your time and efforts.
Challenges in healthcare data warehousing
Data silos and interoperability issues
The power of health data lies in the capacity to analyze and extract insights from it. However, health data is often fragmented due to the complexity of the integration process, which hinders data exchange between teams across the care continuum.
A significant contributor to this issue is the lack of standardization across data sources. Health information is, by nature, heterogeneous because of the various formats used in EHRs, imaging platforms, and other databases. These inconsistencies force healthcare data warehouses to aggregate incongruous records, making it difficult to access a holistic view of patient information needed to deliver high-value, low-cost care that makes healthcare sustainable.
Keeping your HDW unstructured and unusable will result in disorganization and breakability issues further down the data platform pipeline. Applications and integrations, therefore, will pull from potentially faulty data. That’s why many healthcare organizations partner with vendors like Arcadia to bridge the gap between an overflowing data lake and an effectively structured HDW within a holistic data platform framework.
Assurance of data quality and integrity
Just as damaging as fragmented information, erroneous and incomplete data can lead to misguided decision making, duplicative efforts, inefficient use of resources, and missed opportunities to impact a patient’s outcome
Key challenges include:
Missing or incomplete data: Failing to collect or store critical information, such as medication history and social determinants of health (SDoH) data, can impair medical decisions.
Duplicate data: Redundancies resulting from disparate systems can distort population health metrics.
Invalid data: Typos, outdated codes, and inconsistent terminology across systems risk clinical and analytical errors.
Healthcare data warehouses must come fully equipped with quality controls like data cleaning and validation processes. Otherwise, healthcare organizations risk basing their decision-making on unreliable data, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
Compliance and security concerns
Healthcare data warehouses store sensitive patient information, making them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. In fact, the healthcare industry is one of the most frequently targeted industries by cybercriminals, with 80% of healthcare organizations having been targeted by at least one cyberattack in 2024 alone.
Health organizations need a framework for properly handling data to ensure its accuracy, accessibility, and security. A strong data governance framework includes:
Data quality: High-quality data means fewer errors in patient records, more accurate risk adjustment, and better clinical and financial outcomes.
Data management: Effective data management practices should standardize data collection, storage, retrieval, and usage to streamline operations and improve patient care.
Data policies: These rules and guidelines regarding data access and handling ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA and protect patient privacy.
Protecting patient data requires a multi-faceted approach, combining secure technology with organizational policies to safeguard data. As we mentioned earlier in this article, the right healthcare data warehouse will offer encryption and access controls to protect patient data.
Common healthcare data warehouse models
There are a few common HDW models across all providers. Based on their different approaches, they each have their own strengths and drawbacks. Finding the right one will help you bind data — or prepare it for analysis — when it makes the most sense for your organization.
Here are the most common models:
Enterprise data model
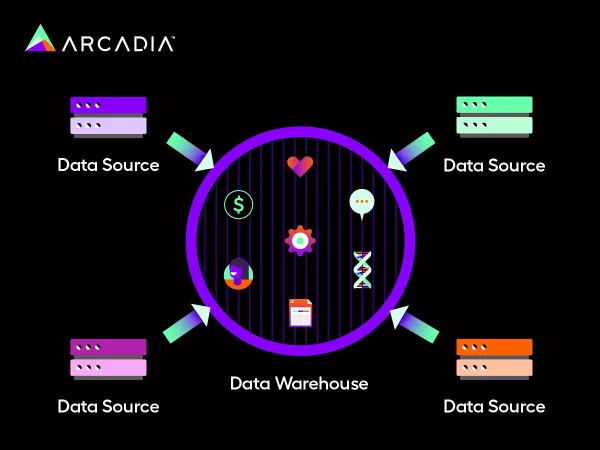
This model represents a top-down approach that most analytics vendors promote, as organizations typically use it when they need additional analytic capacity.
The goal of this model is to create the perfect database from the start by determining everything your organization would like to analyze in advance to improve specified outcomes. For instance, you might decide to prioritize safety and cost-effectiveness and structure your HDW with that end goal in mind.
Although a common model, the enterprise data model promotes an early-binding approach that can delay time-to-value. This means that once the data is bound, making changes is difficult and time-consuming. Therefore, within the ever-changing landscape of healthcare, enterprise models can pose significant challenges when new analyses are needed.
Independent data mart model
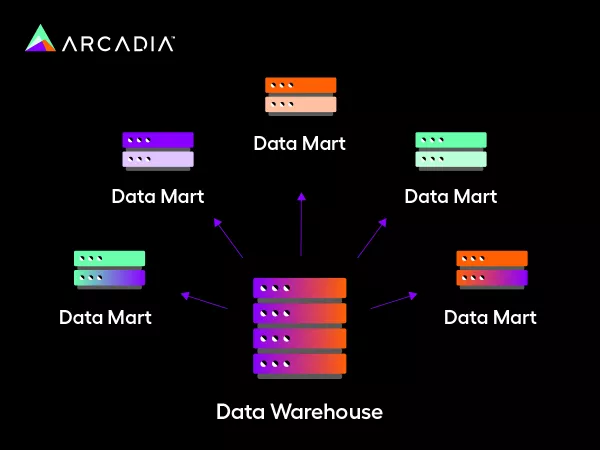
This model advocates for a bottom-up approach and is commonly used for ad hoc analysis since it can build individual data marts for individual departments. For instance, if you need a specific report on patient safety or medical cost containment, your department can build it quickly using this model.
Independent data mart models are inherently smaller and more focused than enterprise data models. They can help your team implement and measure needed metrics much more quickly than enterprise data models. However, independent data marts can also overwhelm systems quite easily and cause data redundancy issues down the line.
Healthcare data warehouse use cases
To visualize the potential impact an HDW can have on your organization, it can be helpful to take a step back and observe how it applies to real-life use cases. In fact, data analytics assist Account Care Organizations (ACOs) in identifying key clinical opportunities that may be hiding in plain sight. That said, here are two use cases to consider:
Providing Value-Based Care for Diabetic Patients
Diabetes afflicts 38.4 million Americans — a staggering 11.6% of the population. Measuring and monitoring this disease is especially important because, if left untreated, it can be a catalyst for several other conditions, such as kidney disease, blindness, stroke, or in the worst case, death. That’s why documenting patient conditions and comorbidities accurately and specifically is an absolute must.
How can an HDW help?
By leveraging SDoH (social determinants of health) factors like risk factors, trends, and pattern identification to cut down on administrative time.
By supporting disease management initiatives, such as glucose level checks and medication adherence.
By providing insights to achieve prevention with appropriate care.
Diabetes is common and involves highly personalized treatment plans to effectively monitor it for intervention. With a robust HDW, your team can confront diabetic challenges head-on while paving the way to value-based care.
Improving end-of-life care
Adequate hospice care gives patients and their families the dignity they deserve during a patient’s final moments. Tracking and visualizing Medicare patients who have passed away can help organizations understand how to improve end-of-life care.
By tracking the cost per patient during their final thirty days, analysts found that:
Patients with adequate hospice care saw regularly increasing costs to the day of their death.
Patients with no hospice care saw costs spiral out of control.
Patients with inadequate hospice care saw a sharp increase in costs that stabilized in their final days.
The ramifications of this data suggest a relationship between adequate hospice care and a more comfortable, higher-quality end-of-life experience.
Next steps: Implementing and leveraging the right platform
As healthcare changes rapidly, a robust data infrastructure is no longer the future of healthcare; it’s the present. Every data point represents an individual, and your organization’s ability to collect, streamline, and analyze each point directly impacts your ability to deliver better care, increased revenue, and reduced costs.
Partnering with an experienced data vendor like Arcadia can help you succeed, no matter your journey in fee-for-service, value-based care, or beyond.
